
Instrument and method for evaluation, study and medical diagnosis in gastroenterology


Attractive

Low cost
Facilitates medical procedure

Protection
PROBLEM
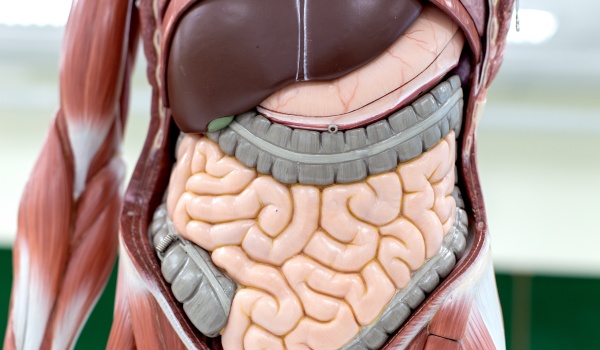
Clinical exams in the gastric area are currently performed by scintigraphy (CGI) and SQUID techniques. The scintigraphy uses radioactive material, requiring a special environment and specialized professionals to perform the exam, besides presenting high operational cost. The SQUID presents the advantages of not being invasive and not using radioactive material, however it has a very high operating cost and needs a magnetically shielded room to perform the exams.
SOLUTION
The use of BCA would bring benefits in the following areas: Medical: low-cost product, portable, non-invasive and ionizing radiation-free product for diagnostic use of the gastrointestinal tract - an alternative for SQUID users and scintigraphy; Pharmaceutical: studies of different parameters of drug delivery in vivo. There is no technique currently used for this purpose; Veterinary: research and diagnosis of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract in dogs and cats. The techniques used in humans are currently not used for this purpose due to the high cost; Animal nutrition: evaluation of the transit of different types of rations in different species of animals; Scientific research: research of the gastrointestinal tract in medium and small animals. The technique is capable of evaluating different physiological parameters in the same animal without the need of the sacrifice soon after the experiment, allowing the realization of new experiments with the same individual.

Idea

Laboratory

Prototype

Scheduling

Market







